Phagocytosis assay
Phagocytosis is a key immune mechanism involves uptake of solid particles into phagosomes, and clearing phagocytosed particles (e.g., pathogens, aggregates of macromolecules, and apoptotic cells). Here, we measured Phagocytosis in whole blood, iPSC Microgila and RAW cells by quantifying engulfed pHrodo bacterial particles.
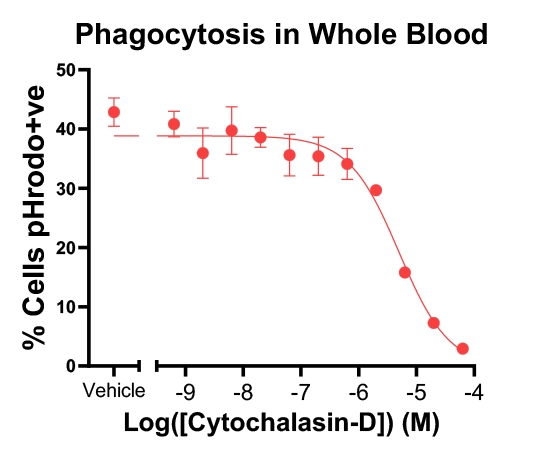
Phagocytosis in human whole blood
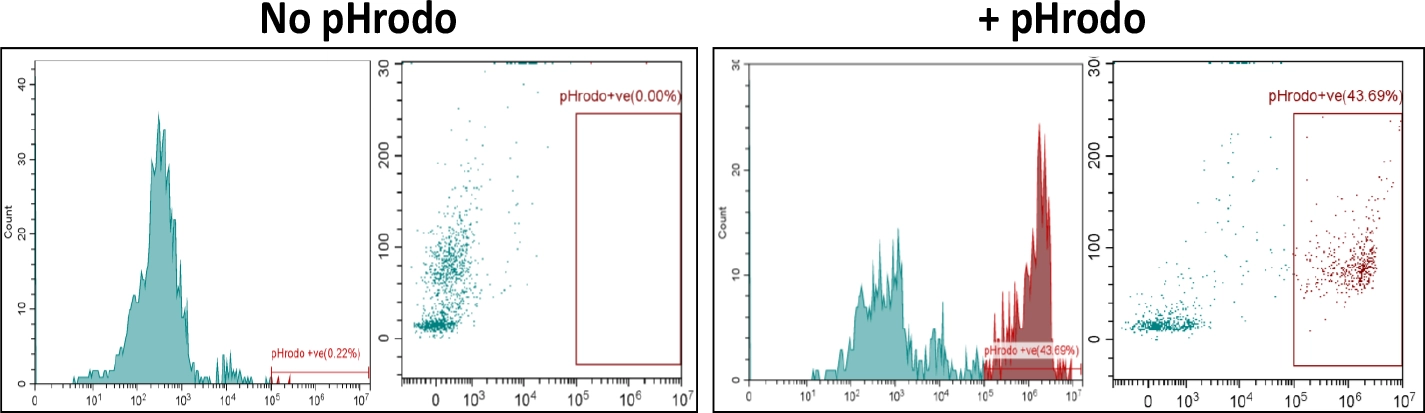
Figure-A: Healthy donor whole blood labelled with pHrodo bacterial particles. Effect of Cytochalasin-D Dose Response Curve on Phagocytosis was measured using Flow Cytometry. Cytochalasin-D showed complete inhibition of phagocytosis in whole blood.
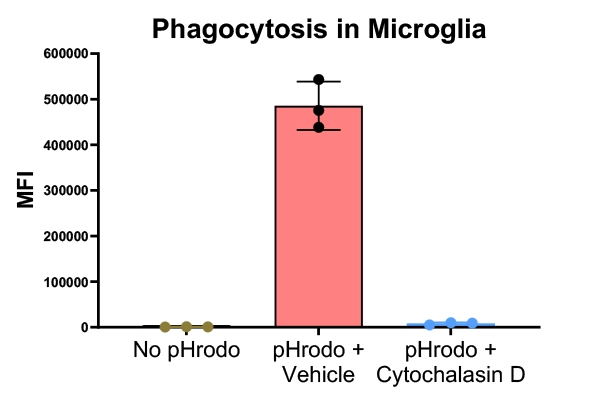
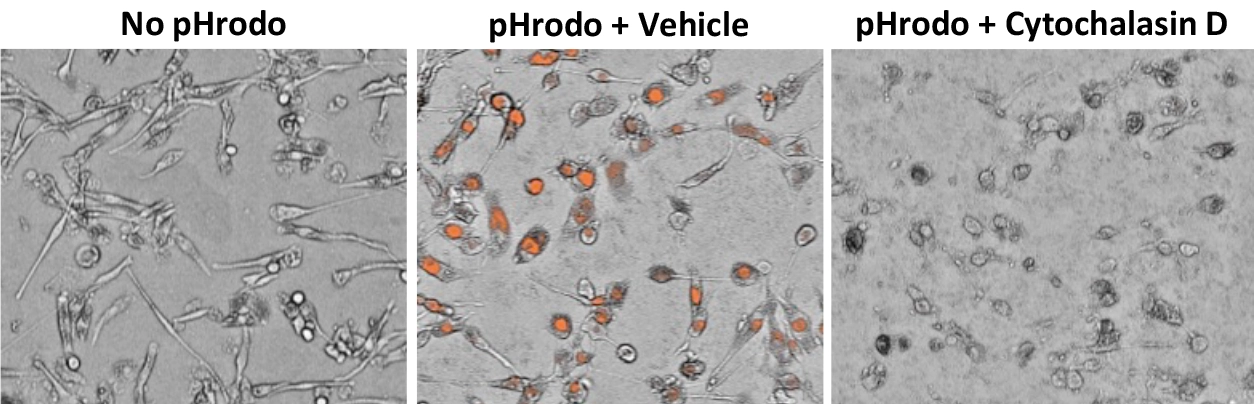
Phagocytosis in iPSC derived Microglia
Figure-B: Matured iPSC microglia were labeled with pHrodo bacterial particles, and phagocytosis was measured in the presence and absence of Cytochalasin-D (10 uM) using cell imaging. Cytochalasin-D showed complete inhibition of phagocytosis in Microglia
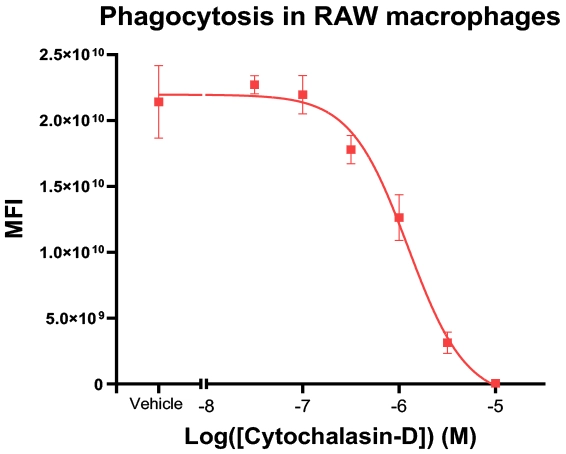
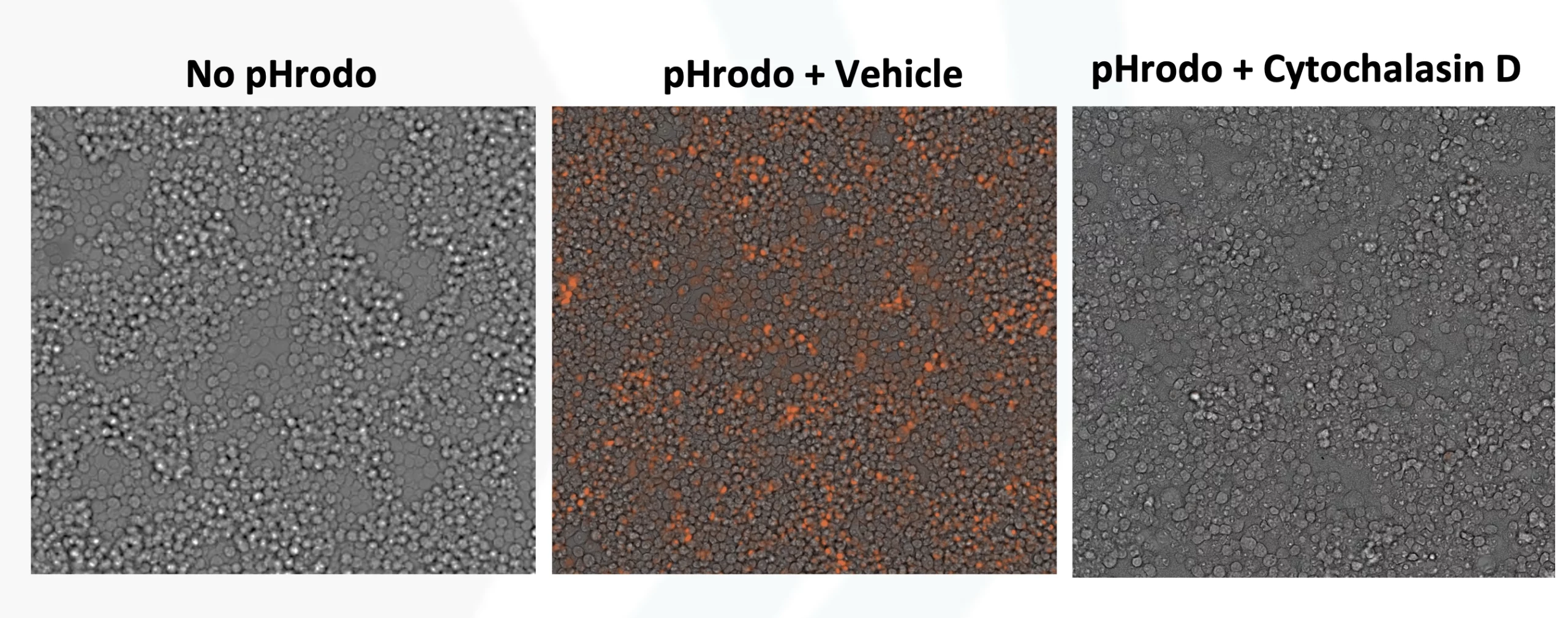
Phagocytosis in RAW macrophages
Figure-C: RAW macrophages were labeled with pHrodo. Effect of Cytochalasin-D Dose Response Curve on Phagocytosis was measured using cell imaging. Cytochalasin-D showed complete inhibition of phagocytosis in RAW cells
Our phagocytosis assays are reproducible and sensitive assay systems, suitable for evaluating compounds that modulate phagocytotic activity.